The rank tells you how much information a matrix contains, while the null space reveals what gets "lost" in the transformation.
In this guide, we'll use MATLAB to compute both properties and verify one of linear algebra's most important theorems.
What are Rank and Null Space?
Rank
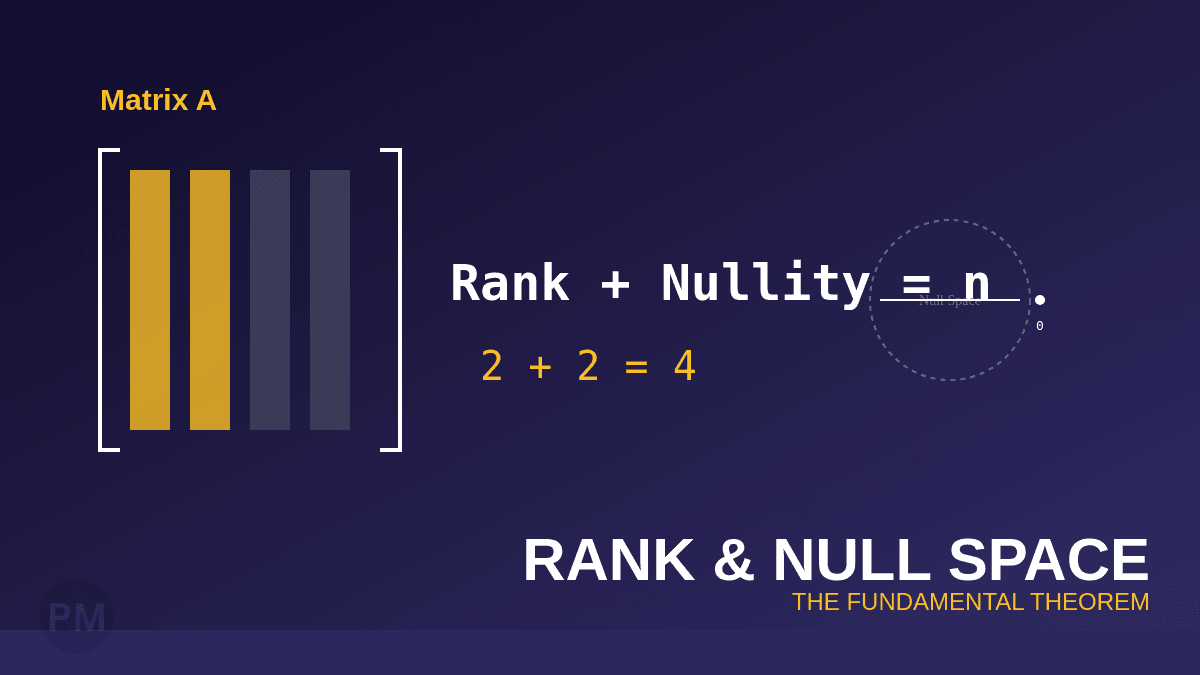
The rank of a matrix is the number of linearly independent columns (or rows). It measures the dimension of the column space.
Null Space
The null space (or kernel) of a matrix A is the set of all vectors x such that:
Ax = 0The dimension of the null space is called the nullity.
The Rank-Nullity Theorem
For any m×n matrix A:
rank(A) + nullity(A) = nwhere n is the number of columns.
Step 1: Enter the Matrix
C = [-1 2 0 4 5 -3;
3 -7 2 0 1 4;
2 -5 2 4 6 1;
4 -9 2 -4 -4 7];This is a 4×6 matrix.
Step 2: Compute the Rank
MATLAB has a built-in function:
rankC = rank(C)Result: The rank is 2.
This means only 2 columns are linearly independent.
Step 3: Compute the Null Space
nullbasisC = null(C,'r')The 'r' flag tells MATLAB to use the rational basis (exact fractions instead of decimals).
Result: MATLAB returns a 6×4 matrix where each column is a basis vector for the null space.
Step 4: Interpret the Null Space
If the null space has 4 basis vectors, the nullity is 4.
Each column of nullbasisC is a solution to Cx = 0.
You can verify this:
C * nullbasisC(:,1) % Should be approximately [0; 0; 0; 0]Step 5: Verify the Rank-Nullity Theorem
rank(C) + size(nullbasisC, 2)Result:
- Rank = 2
- Nullity = 4
- Total = 6 (number of columns) ✓
The Rank-Nullity Theorem is satisfied!
Understanding the Null Space Geometrically
The null space represents all the ways you can combine the columns of C to get the zero vector.
If the nullity is large, it means:
- Many columns are redundant
- The transformation "collapses" a lot of information
Alternative: Using RREF
You can also find the null space manually using RREF:
rref(C)- Pivot columns → correspond to basic variables
- Non-pivot columns → correspond to free variables
Each free variable gives you one basis vector for the null space.
Quick Reference
| Task | MATLAB Code | What it Returns |
|---|---|---|
| Compute rank | rank(A) | Number of independent columns |
| Compute null space | null(A,'r') | Matrix of basis vectors |
| Verify theorem | rank(A) + size(null(A),2) | Should equal number of columns |
Key Takeaways
- Rank = number of pivot columns in the RREF
- Null space vectors correspond to free variables
- Rank + nullity always equals the number of columns
Understanding these concepts is crucial for solving systems of equations, analyzing transformations, and working with subspaces!